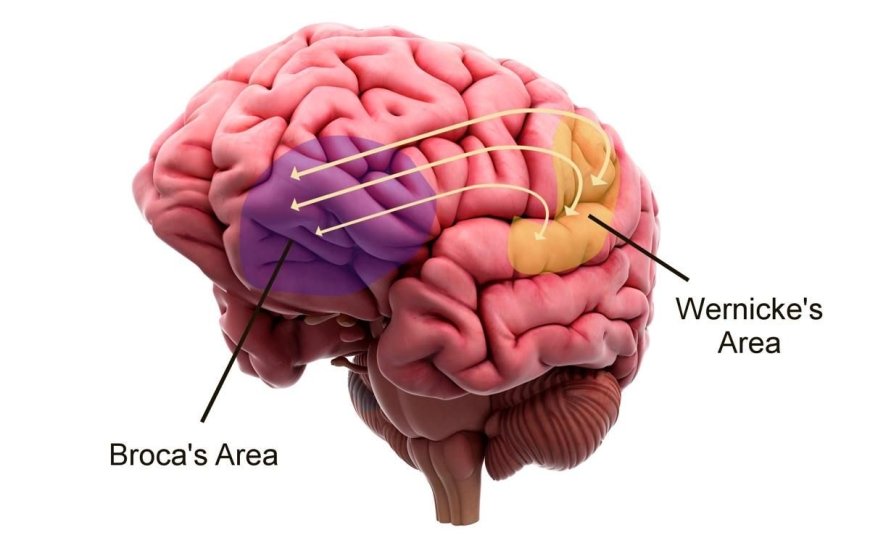
BROCA’S AND WERNICKE’S AREAS
One of the important skills that distinguishes humans from other living things is communication skills. Communicating is an important part of our lives and we provide this communication with language. In order for a person to communicate in a healthy and proper manner, he/she must first produce a language and then be able to make sense of that language. So how do these processes take place in our brain? The production of language, that is, speech, takes place in Broca's area, located in the frontal lobe of the brain. The interpretation of speech takes place in Wernicke's Area, located in the temporal lobe of the brain.
French surgeon Paul Broca made the first study to explain the relation of our brain with language in 1861. After the death of his patient, whom he named "Tan" because it was the only sound he could make, the lesion he found in the left hemisphere according to the brain examinations he made was the beginning of his studies on this subject. In his various studies after that, Paul Broca saw that the left hemisphere has the 'language center' in our brain. For this reason, this area is called Broca's area.
Broca's area is located in the inferior frontal gyrus in the left hemisphere, corresponding to areas 44 and 45 on the Brodmann map. This field, which is of great importance for the expression of language, has two subfields. These; Pars Opercularis and Pars Triangularis. The Pars Opercularis is located in the posterior part of Broca's area and corresponds to Brodmann's area 44. It works with Pars Triangularis to make sense of language, but Pars Opercularis plays a more dominant role in phonological and processing of complex sentences. It has also been discovered that it has an important role in the formation of a person's perception of music. Pars Triangularis, on the other hand, corresponds to Brodmann Area 45 and is located in the anterior part of Broca's area. It plays a role in the interpretation and interpretation of a stimulus, and this area undertakes the task of semantic processing of the language.
The main function of Broca's area, as we mentioned above, is to express the language, but the function of this area is not limited to this. First of all, Broca's area helps us order words according to their semantic integrity while providing vocalization. This allows us to speak in a healthy and fluent way. While it enables us to speak fluently, it works together with regions such as the motor cortex and primary auditory cortex, not alone. In this way, it can coordinate joint organs, namely facial and mouth movements, regulate factors such as prosody, tone of voice, speech speed, and perceive emotional intonations to ensure pronunciation. Also, as we know, our speech and the way we move our hands are interrelated. This relationship is called a gesture. Broca's area interprets the meaning of the gestures we use when speaking to enable the person to communicate more effectively. This interpretation includes animal shapes that we make with our hands in the shade to entertain ourselves or those around us.
If Broca's area is damaged, a condition called Broca's aphasia occurs. The main symptom of this disorder, which causes sudden speech and language disorders, is loss of fluency. Individuals with Broca's aphasia know and feel what they want to talk about, what they want to say, but they cannot express themselves fluently. They have a grammatically incorrect, rhythmless, hesitant speech pattern, but they can only partially understand the language. Therefore, people with Broca's aphasia lose their ability to repeat sentences. In addition, their ability to write and read aloud is impaired.
With his discovery of Broca's area, Paul Broca has led other scientists to do research on the role of the brain in language and speech. A few years after Broca, in 1874, Carl Wernicke discovered a lesion in the left cerebral hemisphere, which corresponds to area 22 on the Brodmann map, in some of his patients with speech problems, and named this area Wernicke's Area.
The most basic function of Wernicke's area is the perception and understanding of language. This area provides the meaning of words by solving the structure of difficult and simple sentences, that is, it undertakes the task of managing language semantics. Therefore, it becomes active when someone else speaks, when we speak ourselves, or when we remember words through our memory, thus processing the language and allowing it to be interpreted. In addition, Wernicke’s area also has important tasks in reading and writing. Therefore, this area works in conjunction with the auditory cortex.
If Wernicke's Area is damaged, a condition called Wernicke's aphasia occurs. Unlike Broca's aphasia, individuals with Wernicke's aphasia have fluency. The person speaks fluently with correct grammar, but the sentence has no integrity of meaning. They make sentences that have no meaning and are not aware of this situation, but they can still form melodic and rhythmic sentences. Individuals with Wernicke's aphasia speak quickly and produce meaningless words. This aphasia creates difficulties in understanding language heard from another person, in addition to difficulties in forming a meaningful sentence. Therefore, Wernicke's aphasia can affect both spoken and written language.
What's Your Reaction?
















































































